Traditional Air Conditioner, Furnace
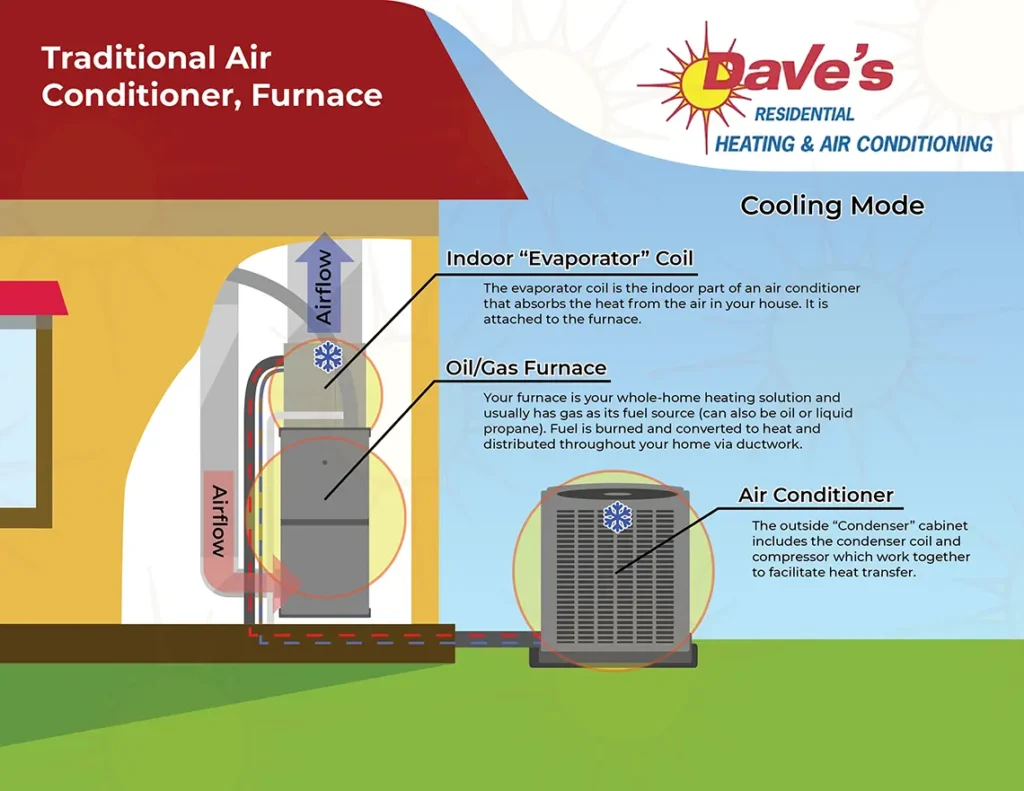
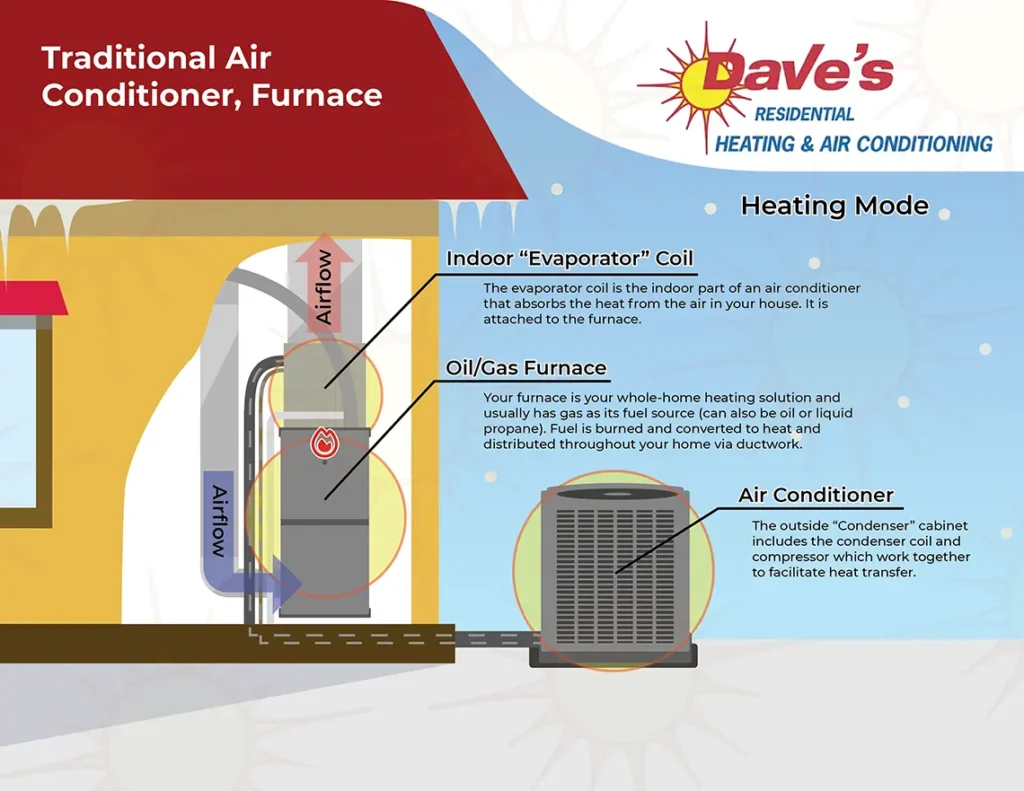
This is a common, effective, and dependable central-air system whereby three distinct pieces of equipment come together to serve your cooling and heating needs, as summarized below:
-
Furnace (heating) Your furnace is your whole-home heating solution and usually has gas as its fuel source (can also be oil or liquid propane). The furnace is located inside the home.
- In a nutshell: Fuel is burned and converted to heat and distributed throughout your home via ductwork.
- Main components of the furnace:
- Ignitor & gas valve (these are very sophisticated pieces of equipment that promote safety)
- Burners (what burns the fuel for conversion into heat)
- Intake fan and heat exchanger (draws air in and converts the energy from the burned fuel into warm air)
- Blower & blower motor (pushes the newly warmed air out into the home via ductwork. Note this blower is also called upon to distribute cool air when the system is in cooling mode)
- Controls (the computer or “brains” of the system which talks to the thermostat and puts everything in motion)
- Media filter (this filters the air as it comes into the system before it gets distributed throughout the house. Check out our Indoor Air Quality solutions for additional options)
-
Air Conditioner (cooling) The air conditioner is made up of the exterior compressor (located outside of the house) which is connected to the indoor coil (located inside the house) via refrigerant lines.
- In a nutshell: The compressor (outside unit) removes heat from the home and the indoor coil (inside the home) cools the air that is distributed throughout your home via ductwork.
- Main components of the air conditioner are:
- Compressor and condenser coil (part of the outside unit)
- Motor and fan (part of outside unit)
- Control board (the “brains” of the compressor, also outside)
- Evaporator coil (“indoor coil,” therefore inside the home)
- Blower & blower motor (technically part of the Furnace but also called upon to distribute cool air when the system is in cooling mode)
- Media filter (this filters the air as it comes into the system before it gets distributed throughout the house. Check out our Indoor Air Quality solutions for additional options)
PROS
- Furnace (gas, oil or propane fuel source) drives more than adequate heating capability even in the coldest of temperatures. Most modern furnaces produce high AFUE efficiency ratings.
- Outside compressor and indoor coil together deliver comfortable cooling temperatures. Most modern units have variable speed capability, high SEER performance and modern thermostat functionality.
CONS
- None really unless your desire is to not use fuel (e.g. gas, oil or propane).
